Insider Threat Detection: Prevention Tools & Techniques

Summary:
-
An insider threat is when someone in an organization misuses authorized access to cause harm by leaking sensitive information.
-
Watch for unusual employee behavior trying to obtain restricted organization data to spot insider threats.
-
Control access, use data protection and security monitoring solutions to prevent insider attacks.
The cost of insider risk has reached an annual average of $17.4 M.
It is quietly draining millions from organizations worldwide. Companies face operational hindrances, damage their reputations, and incur severe regulatory penalties.
So, how do you detect insider threats?
Here, we’ll break down everything about insider threat detection, show you why it fails, and provide suggestions for efficient detection.
In this article
- How to detect insider threats
- Best insider threat detection tools
- Features of insider threat detection tools
- How to prevent insider threats with examples
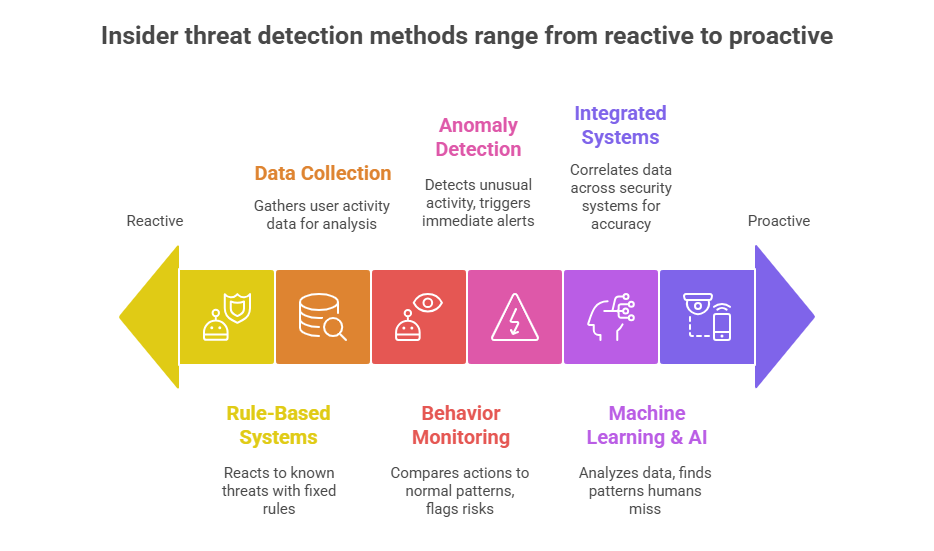
How to Detect Insider Threats?
An insider threat is a security risk that originates from within an organization. From just a janitor to the most trusted partner in an organization, anyone can be an insider threat.
For example, in 2013, Edward Snowden, a former contractor for the National Security Agency (NSA), leaked confidential documents to journalists. It revealed extensive U.S. government surveillance programs. [Source: BBC]
So, let’s check out how you can detect insider threats in any situation:
Data Collection
To detect the insider threat, you will need insightful data. It helps you to assess the user activity, such as file access, emails, and login times.
For instance, it’d be better to use more than one resource and collect effective data. Focus on network logs, endpoint devices, and cloud services.
This way, you build up a clear picture of normal behavior and define some source facts as a reason for the insider threat..
But remember, collecting data is the start. You need to go through a deep analysis of the collected data and create relevance. No matter, it is actually valid or not.
In 2013, Target faced a massive data breach where hackers stole credit and debit card information of about 40 million customers.
Target’s security systems generated alerts about suspicious activity. But these alerts were not acted upon and led to such harm.
Behavior Monitoring
Watch out for the unusual behavior to find the insider threat. Access the files at odd hours or copy large amounts of data. Now, compare the current actions to normal patterns and spot the potential risks early.
By doing this, you can catch suspicious activities before they cause damage.
John Kindervag, creator of the Zero Trust model, has a brilliant remark on this. He said,
“The hallmark of zero trust is simplicity. When every user, packet, network interface, and device is untrusted, protecting assets becomes simple.”
But remember, behavior can change for many reasons, so you must be alert to the false alerts. Better to use a useful method like User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA). It tracks and flags odd behavior and makes this easier and completely fair.
Besides that, nothing can beat human judgment to understand the context behind actions.
Anomaly Detection & Alerting
With Anomaly detection, you can monitor user activity that doesn’t fit normal behavior. The system identifies some unusual activity, like unexpected file downloads or odd login locations. Then, it triggers an alert, and you are notified immediately.
For this, the system first sets a baseline of normal user behavior. Such as access times, data accessed, devices used, and network activity. After that, it monitors the user activity in real time and spots some unusual activity.
The system utilizes advanced algorithms, such as LSTM autoencoders, isolation forests, or cascaded autoencoders. They analyze the behavioral data and detect anomalies.
It could be unusual access to sensitive files or odd login times.
Track user behavior smarter—start using Apploye for real insights
Behavioral Analytics vs. Role-based Systems
To detect the insider threat, you can either go for behavioral analytics or rule-based systems. But both take different approaches to detecting threats.
In the rule-based system, you are getting fixed rules, such as blocking access after repeated failed logins. These are effective enough to find out the risks, but often miss subtle or new threats.
Besides, behavioral analytics defines the user behavior over time. Here, it builds a baseline of normal activities. This is like login times, device use, or data access, and flags anything unusual. All this is done without any specific rule.
It is often seen as a better and efficient option for catching insider threats or growing attacks. This is because it doesn’t depend on any model training or signature maintenance.
But you may need to consider higher false positives at first due to anomaly sensitivity. But in the rule system, it is lower with proper rule configuration.
Role of Machine Learning and AI in Detection
When you want to analyze a large amount of data to detect insider threats, the best way you use machine learning and AI.
They even help you find patterns and behaviors that humans might miss. By this, you can speed up the detection process and reduce the workload on your team.
Also, you can feed the AI with new data and ensure better accuracy than manual methods. It helps reduce the false positives.
Research says that AI-driven security solutions can reduce false positives by up to 95%. Even 69% of organizations using AI can improve their cybersecurity report and ensure faster response times.
Correlation with Other Security Systems (SIEM, DLP, IAM)
Organizations can integrate other security systems to get the most accurate and valuable results for insider threat detection. Such as:
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): It collects and analyzes log data across your network. It includes endpoints, servers, applications, cloud services, and network devices. You can correlate malicious activity with broader security events.
- DLP (Data Loss Prevention): This system monitors and controls the movement of sensitive data across endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. You can detect attempts to steal or leak sensitive information.
- IAM (Identity and Access Management): This is the proper security system an organization can use to ensure that only authorized users can access certain data or systems. Each user gets a digital identity and a role based on their job function, and they must prove their identity to gain access.
Best Insider Threat Detection Tools
Main Features of Insider Threat Detection Tools
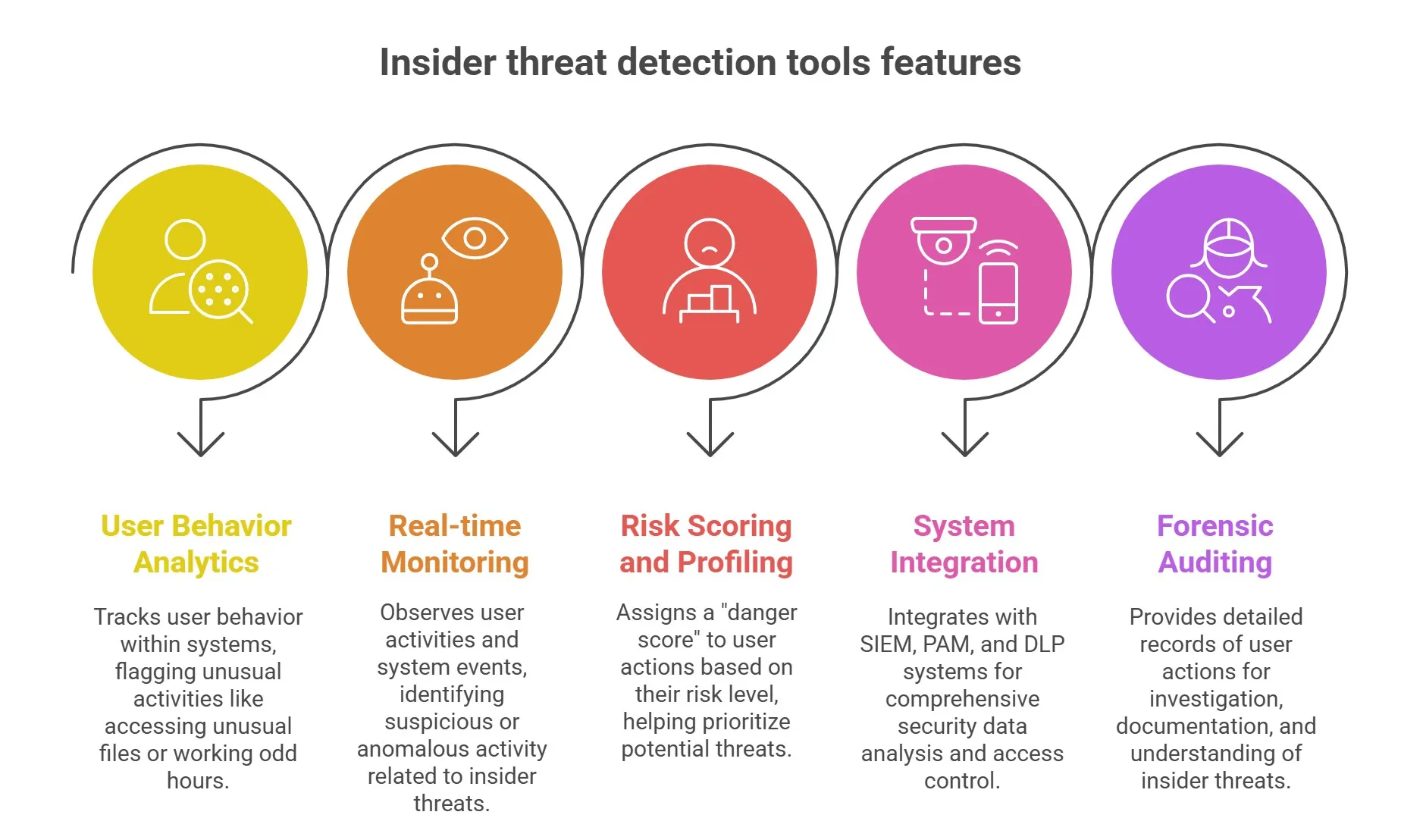
The insider threat detection tools must be equipped with these listed features for effective detection.
User Behavior Analytics (UBA/UEBA)
UBA, or User Behavior Analytics, and UEBA, or User and Entity Behavior Analytics, are the most powerful tools that are designed to track how users behave within your systems.
The system analyzes some important aspects of human behavior. This is like login times, file access, and application use.
When someone acts unusually, like accessing unusual files or working odd hours, the system flags this behavior and alerts you. You can spot insider threats with unusual behavior patterns.
Real-time Monitoring and Alerting
Employee monitoring software and alerting systems are important for insider threat detection, as you will find in Apploye. Using it, organizations observe user activities all the time and system events as they happen.
They can track all the online activity, starting from file access, login times, to data transfers, and much more. It can immediately identify suspicious or anomalous activity that is related to the insider threat.
After detecting the unusual behavior pattern, it generates an alert and helps the company know that there is something fishy.
Activate real-time monitoring to detect insider threats
Top 11 Benefits of Employee Monitoring
Risk Scoring and Profiling
Risk scoring is more likely a “danger score” for a user’s actions based on how suspicious or risky they seem. For instance, you are assigned a numerical value to users or activities. The higher the score, the more likely it is that the action could be a threat.
For example, if an employee downloads a lot of sensitive files late at night, the system will give such behavior a high score. A recent study reveals that risk-based threat detection reduced false positives by 59% and improved true positive detection rates by 30%.
Integration with Other Security Systems (SIEM, PAM, DLP)
Insider threat detection often integrates with systems like SIEM, PAM, and DLP. SIEM collects and analyzes security data across your network.
PAM or Privileged Access Management controls and monitors users by managing legitimate access. DLP or Data Loss Prevention identifies the sensitive data leaks or data breaches you are encountering.
Forensic Auditing and Reporting
Most of the threat detection tools add useful forensic auditing and reporting to investigate, document, and understand insider threats.
They are designed to analyze the threat after it’s detected. You will get a detailed and chronological record of user actions. The report also summarizes findings in easy-to-read formats and makes decision-making far more efficient and fair.
Start using Apploye’s risk scoring to spot insider threats early
How to Prevent Insider Threats with Examples
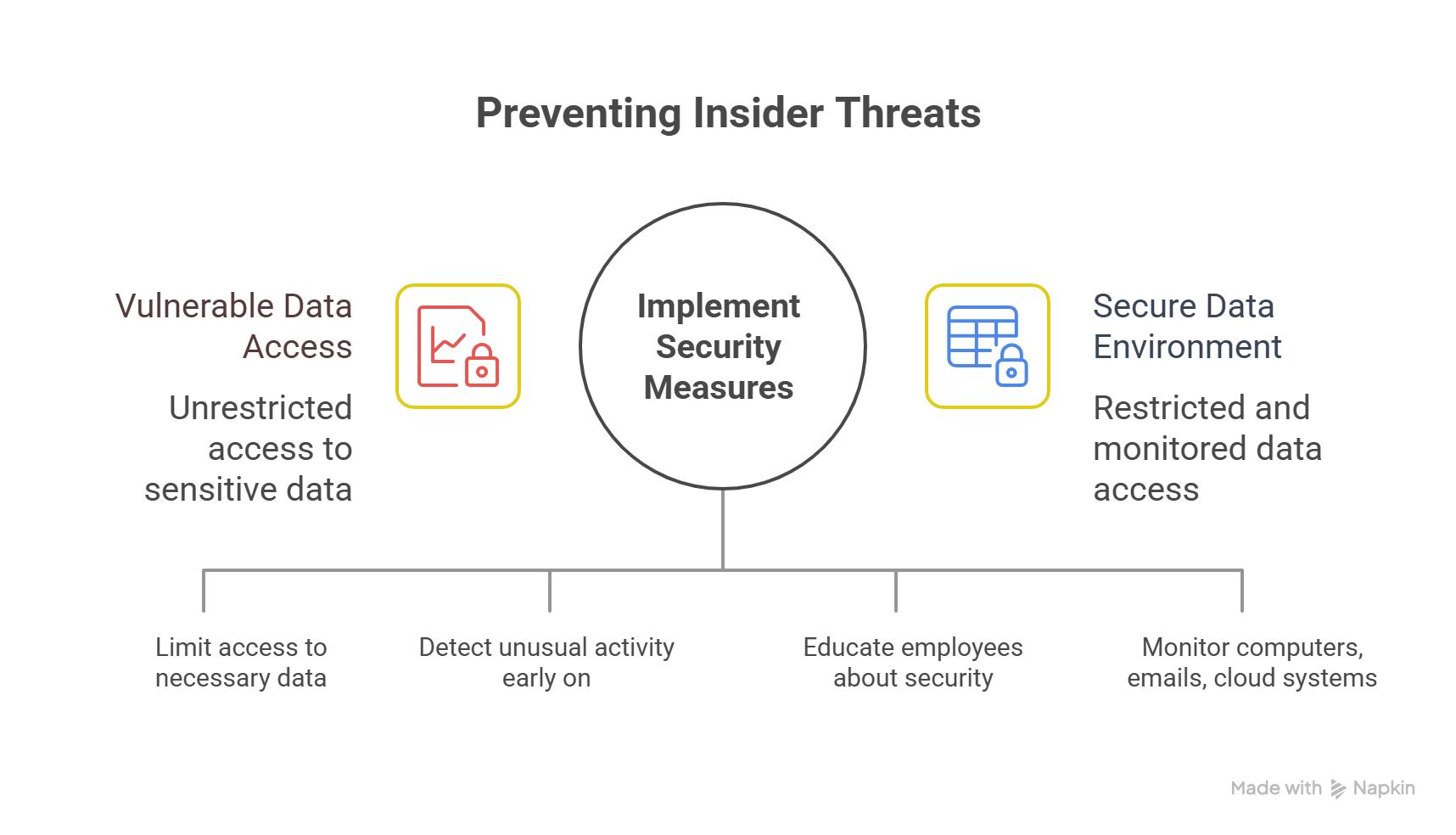
Stop Insider Threats Starts by Controlling Access
First, use the rule of least privilege. This means only give workers access to data they actually need for their job. For example, Capital One's 2019 breach could have been stopped if it had better controls on who could access its cloud systems. [Source: MIT].
Watch How People Behave with Monitoring Software
These tools can spot unusual activity early. In 2021, Waydev, a software company, found strange API activity using user monitoring. This helped them stop a breach before hackers could steal sensitive data. [Source: SecurityWeek]
Train Your Workers Regularly
Analyzing the insider threat mitigation guide of CISA, teaching employees about security helps reduce accidents. It builds a culture where people think about security.
Use Data Protection and Security Monitoring Together
Start using digital solutions to track activities across computers, emails, and cloud systems.
For example, South Georgia Medical Center's monitoring software detected an insider threat in 2021. Their security system immediately flagged an employee downloading patient data to a USB drive. This allowed them to respond immediately and recover the data. [Source: HIPAA Journal]
Conclusion
Detecting insider threats isn’t about quick fixes. It takes careful monitoring, understanding user behavior, and using the right tools. Stay alert, use ongoing detection tools, and build a security-aware team to keep your organization safe
Frequently Asked Questions About Insider Threat Detection
What is an insider threat cyber awareness?
Insider threat cyber awareness involves educating employees and stakeholders about the risks posed by individuals within an organization who may misuse their access. It helps identify suspicious behaviors, promotes secure data handling practices, and builds a culture of vigilance against internal cyber threats.
What is threat detection?
The threat detection is the complete process of finding potential security risks or malicious activities within a system or network. Organizations should spot the risks earlier to prevent data breaches or damage.
What is an indicator of insider threat?
An indicator of insider threat would be any unusual or suspicious behavior by an employee. Like any individual typing to access sensitive data without authorization, downloading large amounts of information, or working odd hours without a clear reason.
What are the three types of insider threats?
The three main types of insider threats include malicious, negligent, and compromised insiders. Malicious is one who misuses their authorized access to cause harm. Negligents are well-meaning employees who are causing damage without intention. Compromised insiders are those whose accounts are hijacked by external attackers.
Why are insider threats difficult to detect?
Insider threats are often hard to detect as insiders already have legitimate access, and their actions seem normal behavior. Employers find their motives complex and unpredictable. Without the proper context or advanced tools, it is challenging to differentiate harmful actions from routine ones.
Who are your insiders?
The insiders are those who already have legitimate access to your organization's systems and data. They are likely employees, vendors, third-party service providers, or business partners with access to internal systems.
Who is at risk of insider threats?
It would be anyone within an organization who is at risk of insider threats. This is like employees, contractors, vendors, and partners who have access to sensitive systems or data.
How to prevent and stop an insider threat?
To prevent insider threats, it is best if you can ensure strict access controls, check user behavior, and provide regular security training. Plus, with the use of advanced detection tools, you can spot suspicious activities.
What advantages do insider threats have over others?
Insider threats have access to sensitive systems and data, which often makes it harder to track their attack. Often, they have a full understanding of the internal processes and security measures, which increases their chances of success.
What are the risks caused by an insider threat?
Insider threats lead to financial loss and significant damage to the company's reputation. It often creates unforeseen legal problems that the company has to bear in the long run.
How do you identify and prevent insider threats in your organization?
To identify insider threats, unusual behavior, or access to sensitive information. Use strong access controls, assess activities, and provide regular security training to employees to prevent such threats.
How can organizations manage and mitigate the risk of insider threats?
Organizations can manage insider threats by implementing clear security rules and monitoring their user activities. You can also use the tools to detect unusual behavior. Conducting thorough employee training programs to help everyone understand its consequences and ensure a credible working environment.
How can organizations use artificial intelligence for threat detection?
Utilizing artificial intelligence can be an effective process to spot unusual patterns or behaviors that may signal a threat. It analyzes the large amounts of data in real-time and detects insider threats faster with more accurate versions.
How can organizations detect and prevent insider threats in a cloud environment?
Organizations can monitor user activity across cloud services using tools like UEBA and DLP, enforce identity and access management (IAM), and apply real-time anomaly detection. Regular audits, least-privilege policies, and integrated security systems also help prevent insider misuse in cloud platforms.
What are the early indicators of a potential insider threat?
Early signs include accessing sensitive data without a clear need, working unusual hours, bypassing security protocols, or downloading large volumes of information. Behavioral changes like disgruntlement or secrecy may also signal risk and should be monitored alongside digital activities.
Why are insiders potentially the greatest cybersecurity threat to an organization?
Insiders already have authorized access to systems, making it easier for them to bypass security controls. Their knowledge of internal structures and processes allows them to carry out harmful activities more subtly and effectively than external attackers.
What industries are most at risk of insider threats?
Sectors like finance, healthcare, government, and technology are at higher risk due to the sensitive data they handle. Organizations with large remote workforces or access to intellectual property are also frequent targets of insider threats.
How do boundary violations, life narrative factors, and psychosocial issues play a role in identifying potential insider threats within an organization?
These human factors can signal internal instability or dissatisfaction. For example, personal grudge, financial distress, or a perceived lack of recognition may lead employees to justify unlawful actions. This makes behavioral monitoring essential for early detection.
In what ways can digital forensics be used to investigate insider threats?
Digital forensics analyzes logs, file access patterns, and communication trails to trace unauthorized actions. It helps reconstruct events, gather evidence, and understand how and why an insider exploited their access, which supports both mitigation and legal action.
How is AI revolutionizing threat detection in cybersecurity?
AI enables real-time analysis of vast data sets, detects subtle anomalies in behavior, and learns continuously to improve threat identification. It significantly reduces false positives and response times, making detection more proactive and efficient.
What are the types of tools/software that prevent insider threats?
Key tools include User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), and Privileged Access Management (PAM). Employee monitoring and AI-driven platforms also enhance detection and response capabilities.

